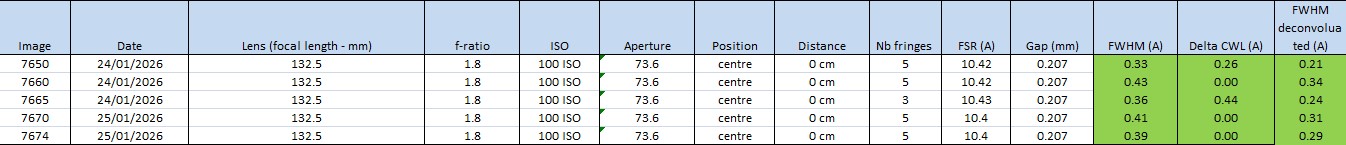
| Test method | f-ratio | Surface sampled | FSR | FWHM | Delta CWL | Note | |
| Heliostar 100 mm (#1) |
Spectro - SHG700 (fc=125 mm, fi=200mm, 2400 l/mm, 10 micron × 4.5 mm slit) IMX585 Etalon left inside the Heliostar 76 |
collimated |
full aperture |
||||
| Hydrogen lamp + diffuser | full aperture | 10.4 A | < 0.35 A when tuned on Ha < 0.25 A when not compressed |
. + 0.44 A |
|||
| Blocking Filter | Solex
(fc=80 mm, fi=125mm,1200 l/mm, 10 micron × 4.5 mm slit) IMX585 |
collimated | FWHM = 7.7 A BW at 10% peak = 9.8 A |
3-cavity filter |
Compression mechanism:
- The air-spaced etalon is tuned by compression. Compression is applied to the center of the etalon.
- In any case, the central pin is hold by a three-leg spider supported by the threaded ring (approximated pitch = 1 mm).
- The tuning of the CWL is very smooth.
- Rotating the knob CW (seen from the focuser), reduce compression and shifts the central wavelength to the red.
- The free aperture is 60 mm and central is 10 mm, or 13%, which means that there is no impact of obstruction on the contrast of images.
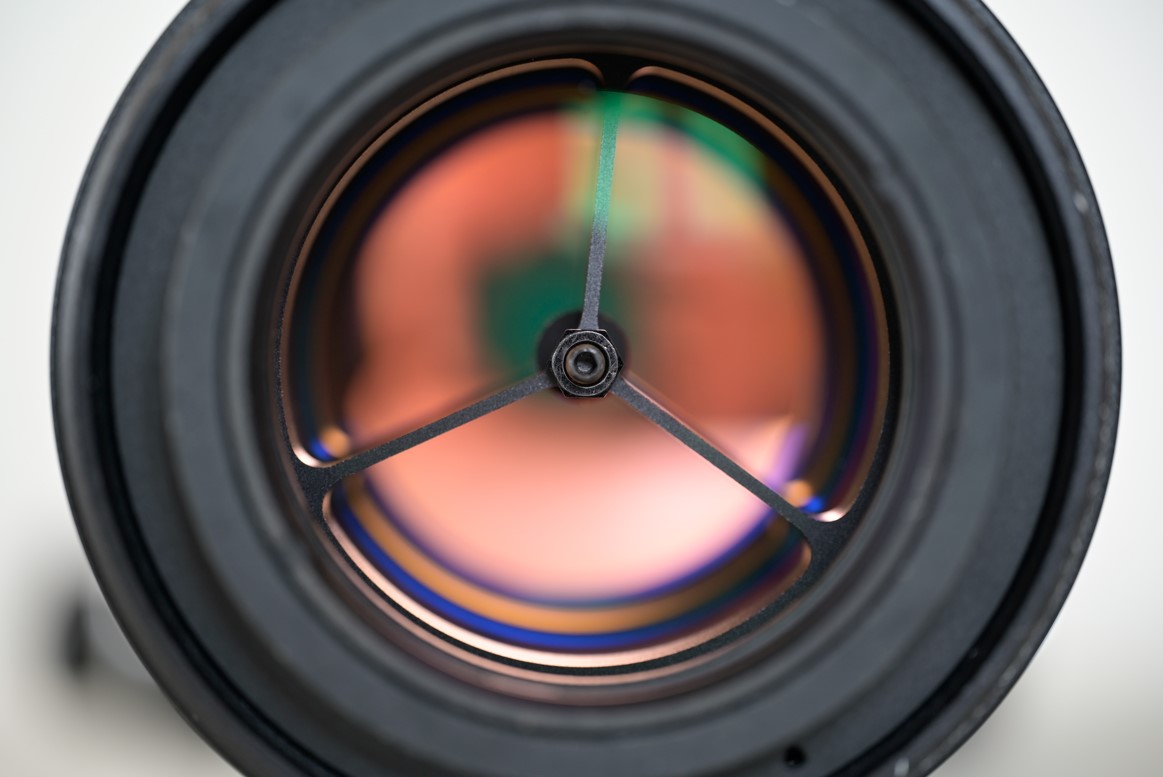


Etalon and three-leg spider supporting the central pin of the compression system seen from the side facing the Sun.
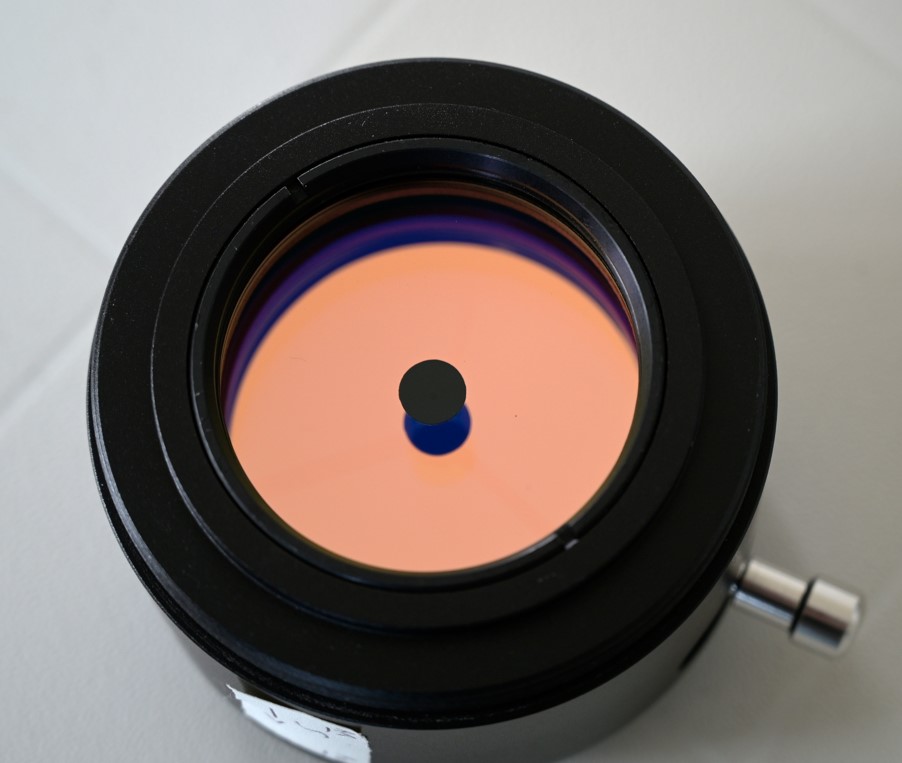


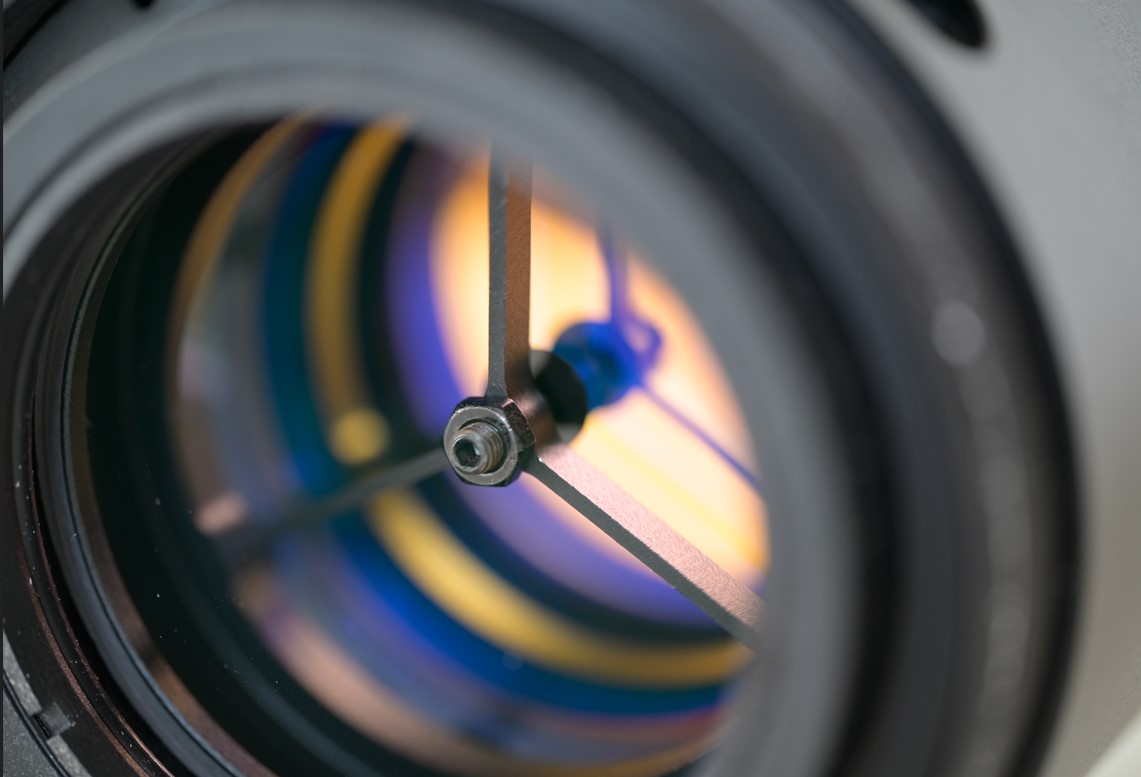
Etalon seen from the side facing the focuser. Note the possible rectangular central spacer (left image).
- The air-spaced etalon is tuned by compression. Compression is applied to the center of the etalon.
- In any case, the central pin is hold by a three-leg spider supported by the threaded ring (approximated pitch = 1 mm).
- The tuning of the CWL is very smooth.
- Rotating the knob CW (seen from the focuser), reduce compression and shifts the central wavelength to the red.
- The free aperture is 60 mm and central is 10 mm, or 13%, which means that there is no impact of obstruction on the contrast of images.


Etalon and three-leg spider supporting the central pin of the compression system seen from the side facing the Sun.


Etalon seen from the side facing the focuser. Note the possible rectangular central spacer (left image).
Optical design
- the air-spaced etalon is in a collimated beam (with is a divergent lens in front of the etalon and a convergent lens after the etalon).
Measurement in diffuse light using a hydrogen discharge lamp
In this test, the Fabry-Perot etalon is used as an interferometer. The whole the surface of the etalon is sampled. The FWHM, FSR and air-gap are derived from the measurements of the fringe system.
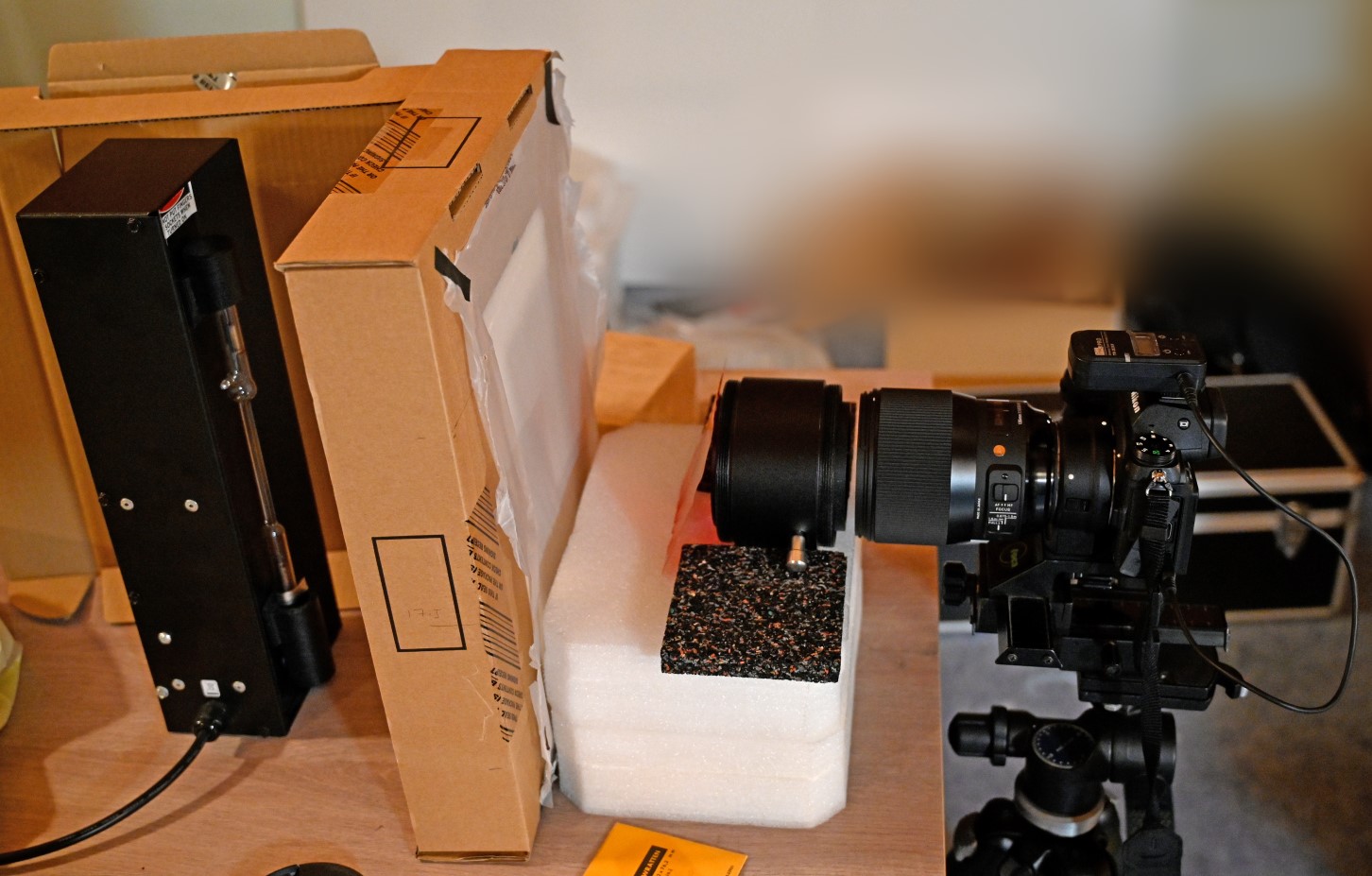
The etalon is removed from the Heliostar 100. The divergent is removed. The convergent lens is kept since is has no impact on the test. The optical setup is:
Optical setup:hydrogren lamp => diffuser => W25 filter (to remove continuum from hydrogen lamp => convergent lens next to the etalon (no impact on the fringe system) => etalon (without divergent collimating lens, the side facing the Sun face the telephotolens) => 135 mm f/1.8 Sigma lens (focused to the infinite) with Nikon Z7 II.

1 - Etalon tuned on Ha
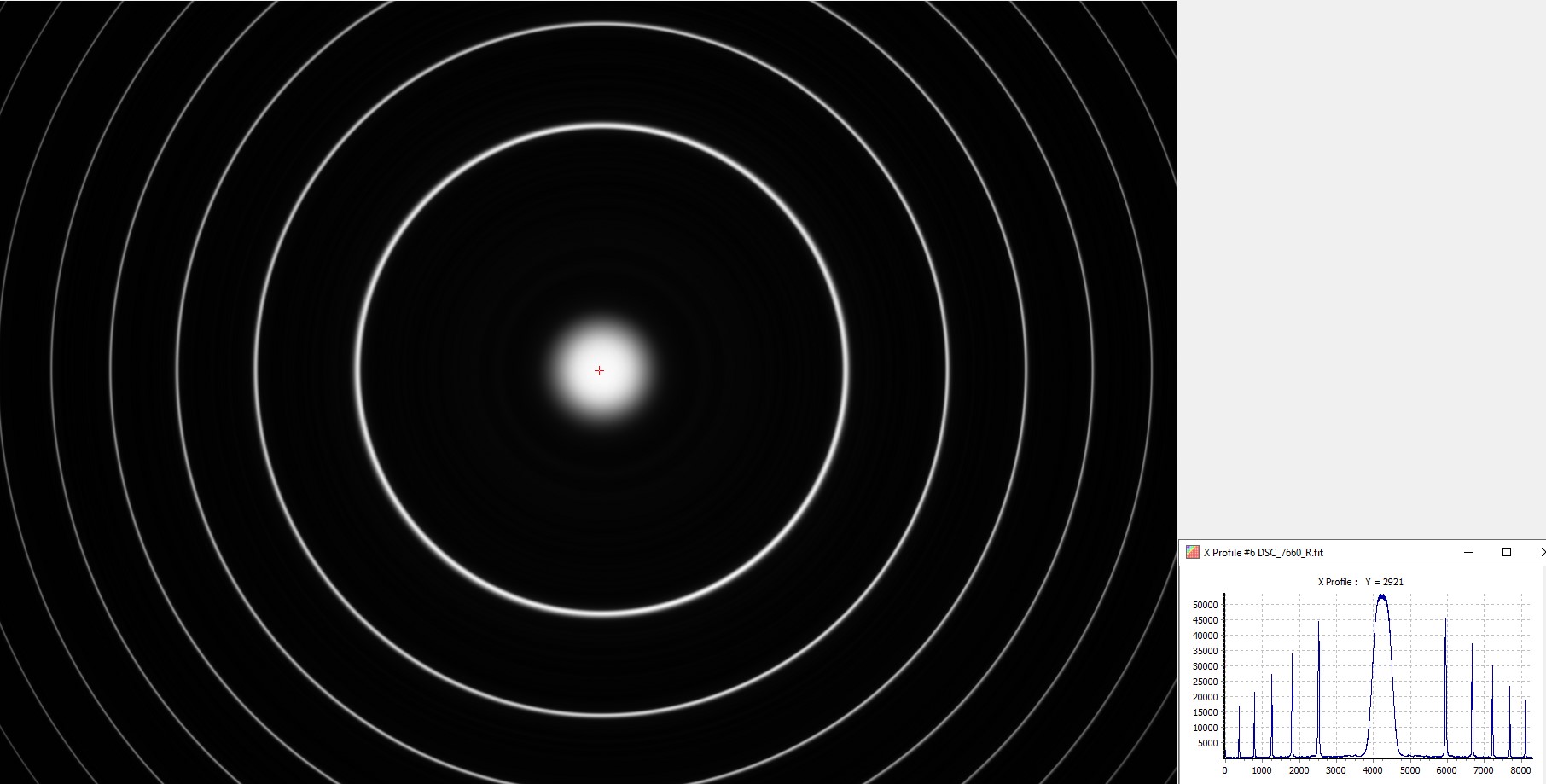
Interference fringes obtained with the etalon tunedo n t Ha.
Sigma 135 mm f/1.8 - Nikon Z7 II - RAW mode - 14-bit acquisition - 4 s exposure time - 100 ISO
Fit of the inteference profile with Fityk using Voigt functions:
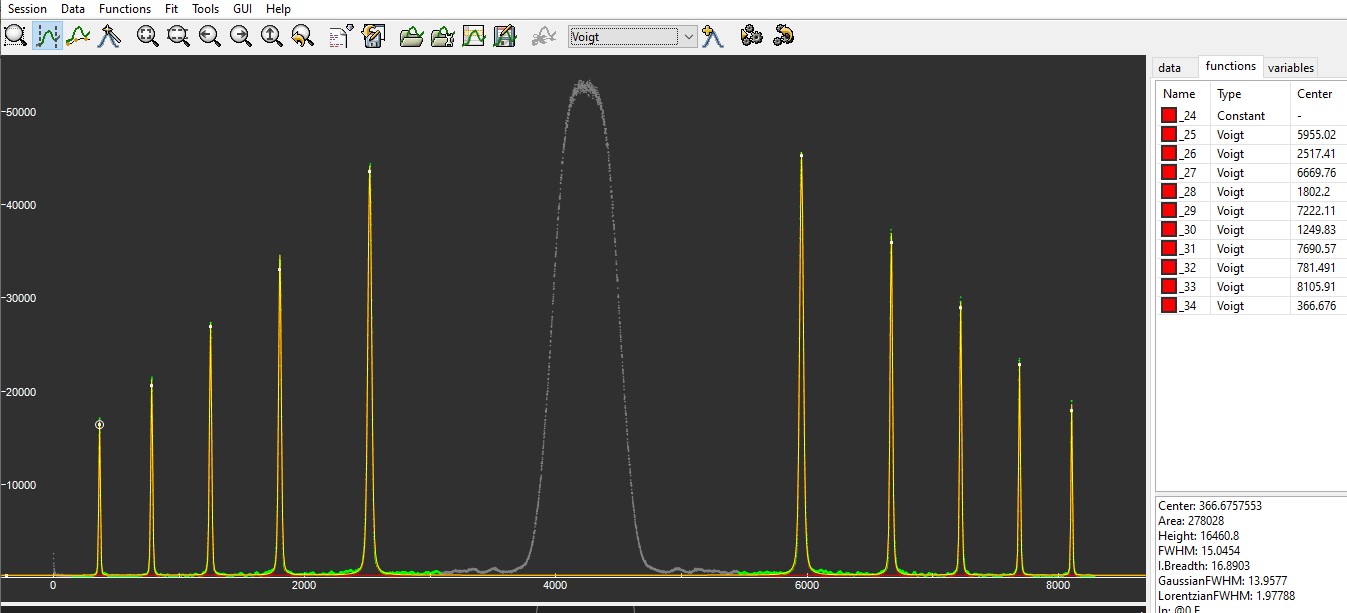
Raw FWHM = 0.43 A.
Deconvoluated FWHM = 0.34 A (based on measured FWHM of hydrogen lamp = 0.263 A).
FSR = 10.4 A.
Air-gap is 0.20 mm ± 0.01 mm
2 - Etalon at Ha + 0.26 A
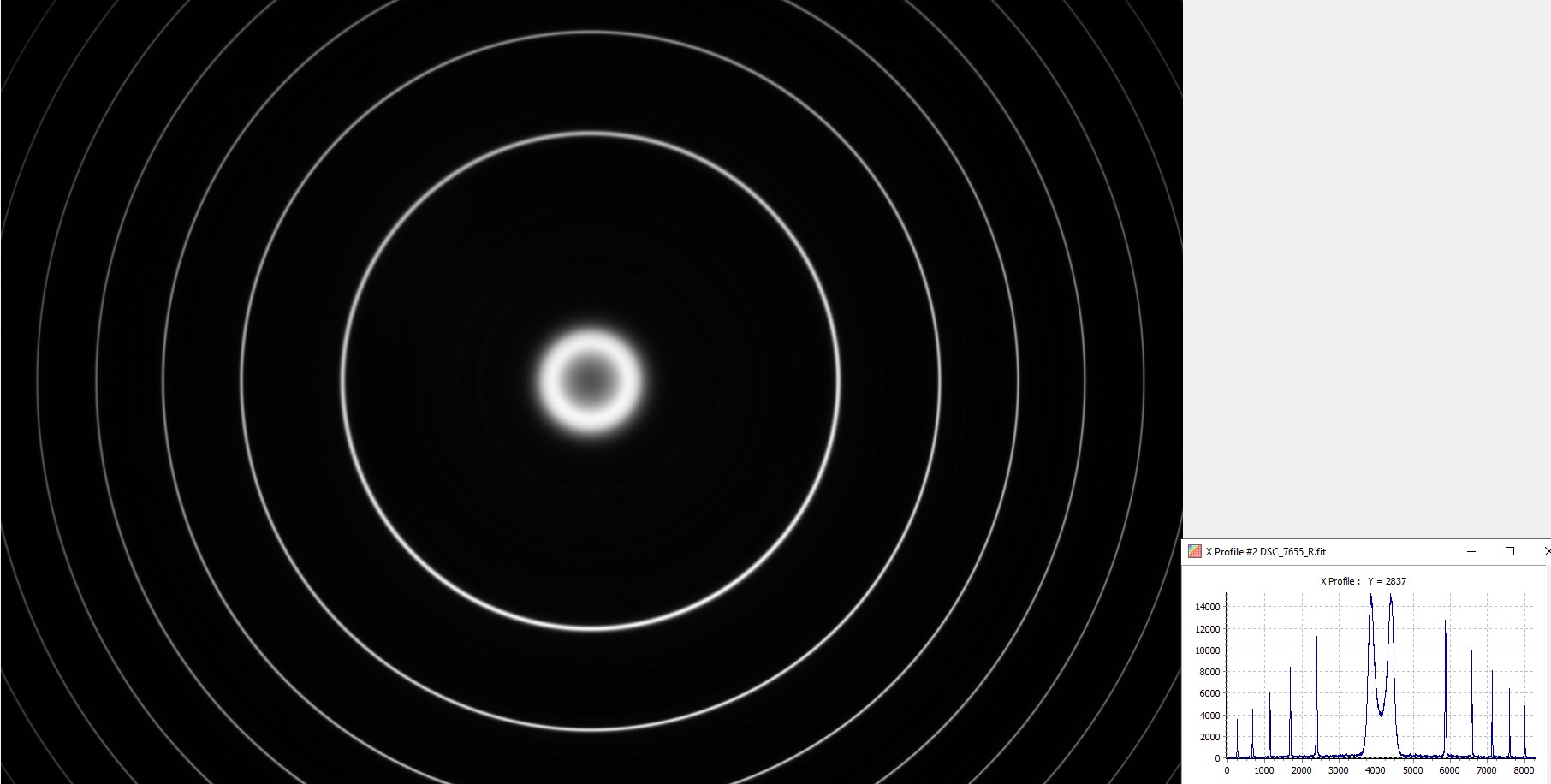
Interference fringes obtained with the etalon tuned at Ha +0.26 A.
Sigma 135 mm f/1.8 - Nikon Z7 II - RAW mode - 14-bit acquisition - 1 s exposure time - 100 ISO
Fit of the inteference profile with Fityk using Voigt functions:
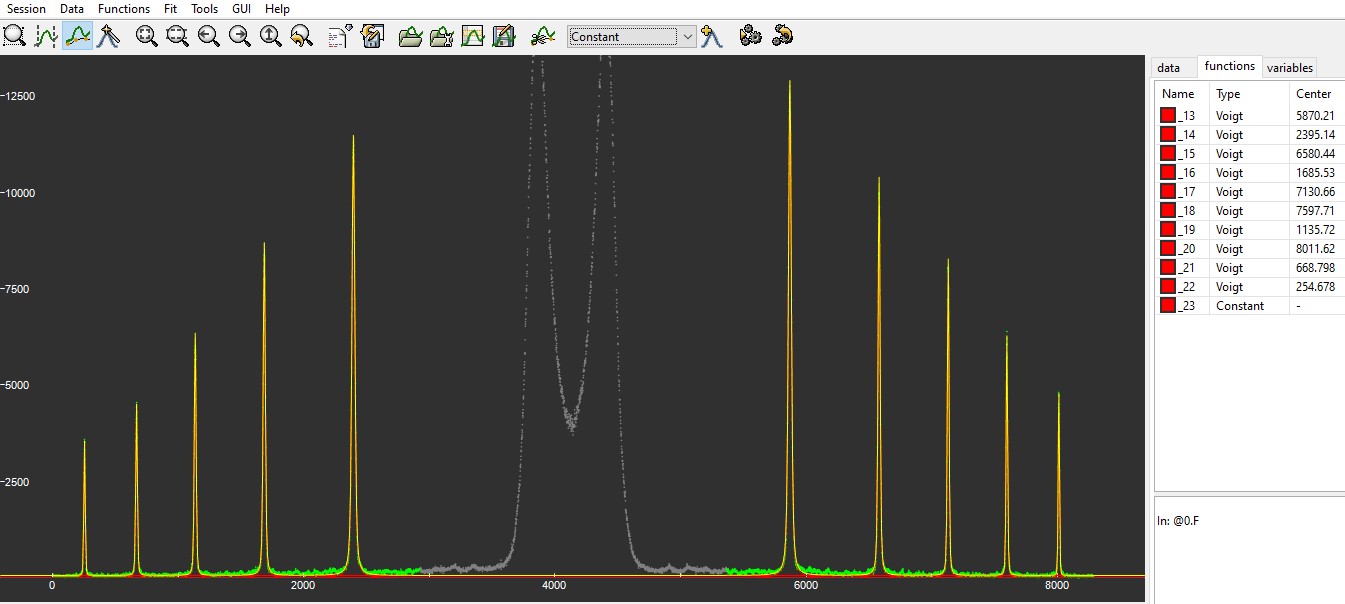
Raw FWHM = 0.33 A.
Deconvoluated FWHM = 0.21 A.
FSR = 10.4 A.
Air-gap is 0.20 mm ± 0.01 mm
3 - Etalon not compressed (CWL = Ha + 0.44 A)

Raw FWHM = 0.36 A,
deconvoluated FWHM = 0.24 A.
Three different measurements were made with the etalon tuned on Ha in order to evaluate the dispersion of results. FWHM was from 0.39 A to 0.44 A (i.e within ± 0.03A)
Qualitative
and quantitative estimation of the uniformity of the etalon and
visualization of the impact of mechanical compression on the FWHM
Principle:
- The test evaluates qualitatively the uniformity of transmission of the etalon over its full aperture. Non uniformities can come from coating non uniformities, surface roughness, non uniformity of the cavity gap, etc.. These transmission non uniformities turn into non uniformities of CWL and FWHM over the aperture of the etalon.
- The etalon is illuminated by a collimated beam coming from an hydrogen discharge lamp. The uniformity of the etalon is examined using a 135 mm f/1.8 lens focused on the etalon surface.
- If the etalon were completely uniform, its brightness would remain constant across its entire aperture. Plages are brighter when the local CWL on Ha. As the local CWL shifts from Ha, the plages become darker.
Though qualitative, the test is very sensitive. Additionally, it is all the more sensitive that the FWHM of the etalon is small.
Important note:
- Uniformity of the etalon as no impact on the sweet spot. These are completely different issues. Non uniformity only impacts the FWHM and CWL of the etalon.
- The test evaluates qualitatively the uniformity of transmission of the etalon over its full aperture. Non uniformities can come from coating non uniformities, surface roughness, non uniformity of the cavity gap, etc.. These transmission non uniformities turn into non uniformities of CWL and FWHM over the aperture of the etalon.
- The etalon is illuminated by a collimated beam coming from an hydrogen discharge lamp. The uniformity of the etalon is examined using a 135 mm f/1.8 lens focused on the etalon surface.
- If the etalon were completely uniform, its brightness would remain constant across its entire aperture. Plages are brighter when the local CWL on Ha. As the local CWL shifts from Ha, the plages become darker.
Though qualitative, the test is very sensitive. Additionally, it is all the more sensitive that the FWHM of the etalon is small.
Important note:
- Uniformity of the etalon as no impact on the sweet spot. These are completely different issues. Non uniformity only impacts the FWHM and CWL of the etalon.
Optical setup:
hydrogen lamp => 3.0 mm aperture stop placed at the focus of the convergent lens of the etalon of the Heliostar 100 (meaning the light beam incident on the etalon is collimated, with a f-ratio = f/135 given the focal length of the convergent lens) => etalon with its convergent lens, but without its divergent lens => 135 mm f/1.8 Sigma lens => Nikon Z7 II with focus set on the surface of the etalon
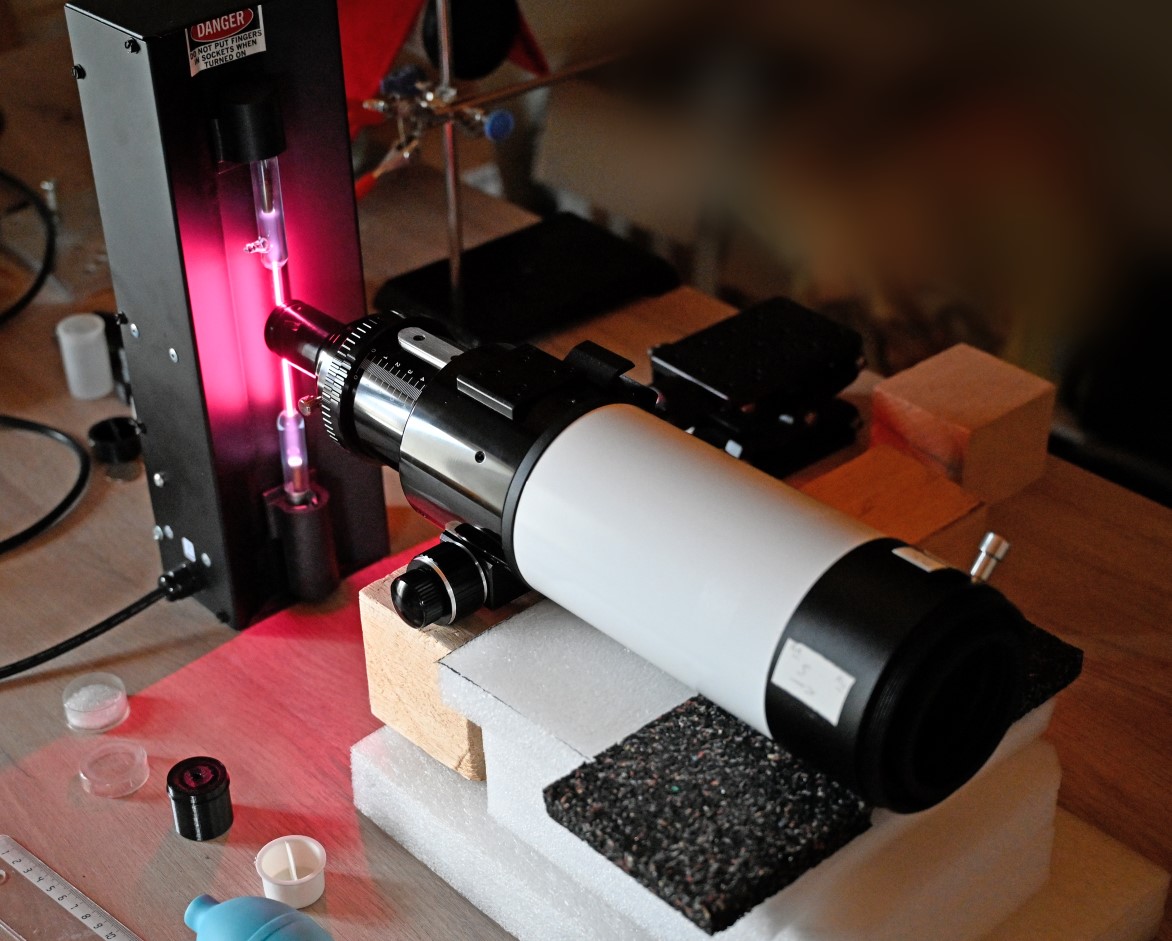

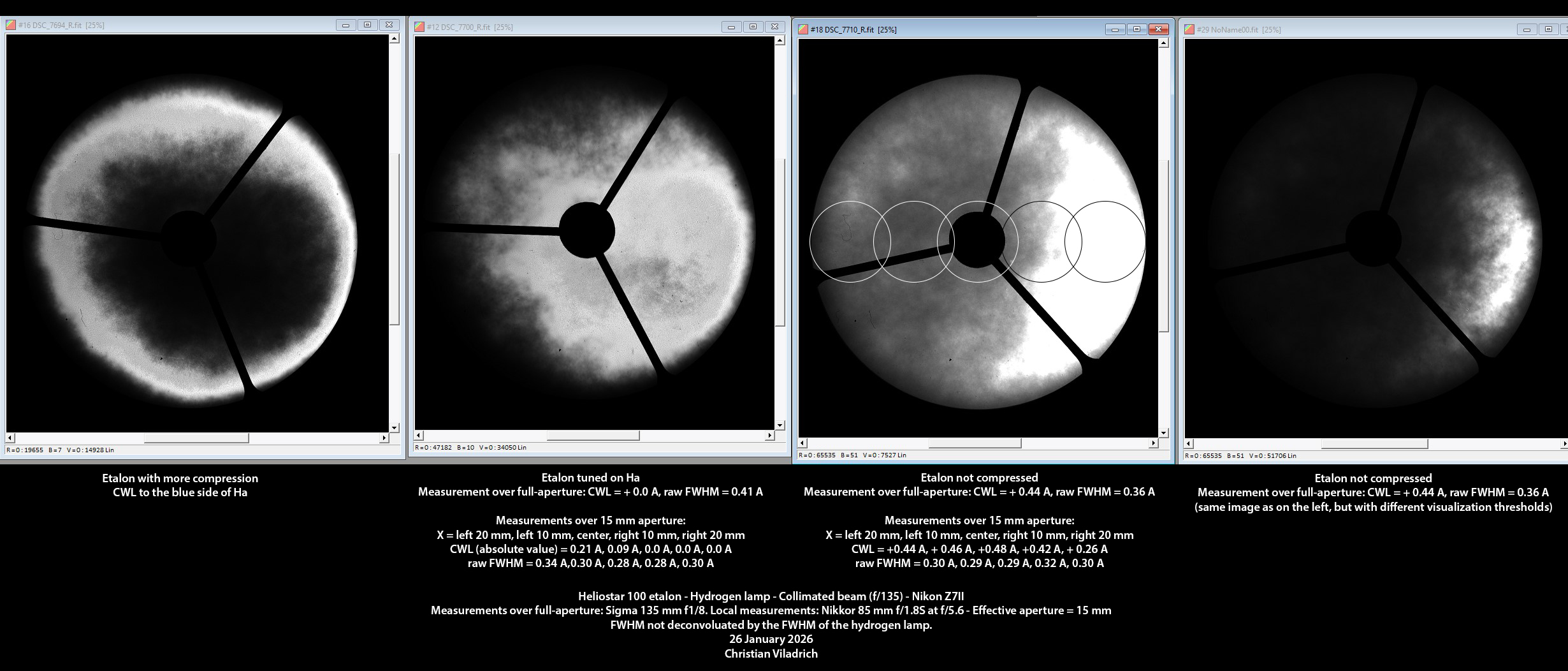
hydrogen lamp => 3.0 mm aperture stop placed at the focus of the convergent lens of the etalon of the Heliostar 100 (meaning the light beam incident on the etalon is collimated, with a f-ratio = f/135 given the focal length of the convergent lens) => etalon with its convergent lens, but without its divergent lens => 135 mm f/1.8 Sigma lens => Nikon Z7 II with focus set on the surface of the etalon


Comments:
- The bright areas are the areas on Ha (or very close). The dark areas are away from Ha.
- The compression of the etalon increases from the image on the right (Ha +0.44 A, no compression) to the image on the left. We can see the spider legs rotating accordingly.
- The two images on the right are actually the same image displayed with different visualization thresholds, with no etalon compression.
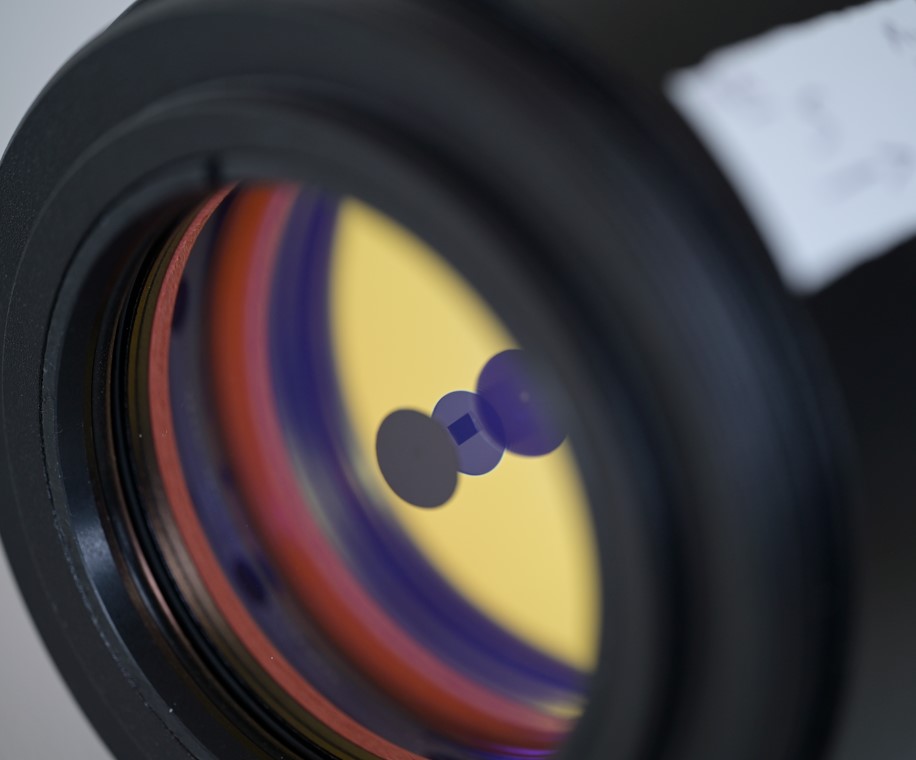
- Local measurements over an aperture of about 15 mm were done with the etalon tuned to Ha, and the etalon not compressed. The approximate positions are given by the circles on the second image on the right.
- When there is no compression (position Ha + 0.44 A), the CWL of the etalon is uniform to ± 0.02 A, except on its right side where the CWL shifts by about 0.2 A.
- When the etalon is tuned to Ha, the CWL of the etalon is still quite good with about 3/4 of the aperture on Ha. On the left side there is a CWL shift of about 0.2 A,
- With more compression, only the outer rim is on Ha.
- Note that non uniformities come from variations of CWL (about 0.2 A). On the opposite, the FWHM is pretty uniform with only minor variations (about ±-0.02 A).
- All in all, the CWL non uniformities are very small, which explains the very small value of the FWHM.
Measurement of the FWHM of the Blocking Filter using a diode as a light source
Optical setup: diode => 5 mm aperture hole => 55 mm f/8 collimator => Blocking Filter => Solex f_c = 80 mm, f_im= 125 mm, 1200 lpmm, IMX585
dispersion = 0.192 A/pixel
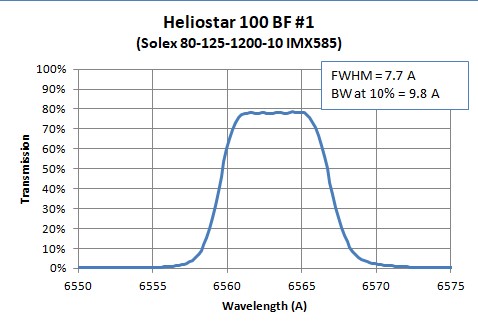
Transmission is measured to about ±5%.
The filter is 3-cavity (BW at 10% peak transmission < 1.5 × FWHM)
Optical setup: diode => 5 mm aperture hole => 55 mm f/8 collimator => Blocking Filter => Solex f_c = 80 mm, f_im= 125 mm, 1200 lpmm, IMX585
dispersion = 0.192 A/pixel

Transmission is measured to about ±5%.
The filter is 3-cavity (BW at 10% peak transmission < 1.5 × FWHM)